Animal Cell Culture
Tissue culture is the general term for the removal of cells, tissue, or organ from an animal and their subsequent placement into an artificial environment suitable for cell growth.
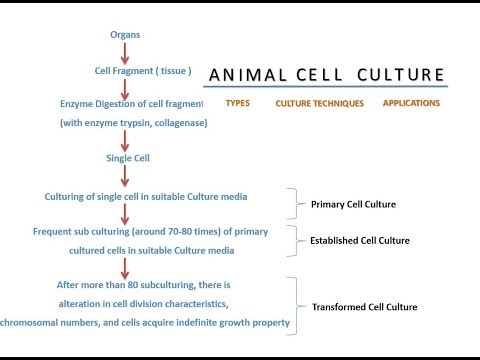
When the cells are removed from the organ fragment before culture, separated in single cell condition and then placed in suitable culture media, this method is called animal cell culture.Primary Cell Culture
When the cells are surgically removed from an organ and placed into a suitable culture environment, they will attach, divide and grow. This is the first step to establish a cell culture. This is called primary cell culture.
There are three basic steps to establish primary cell culture;(a) Isolation of Cells
In this step, cells are isolated from any particular tissue.
(b) Disaggregation of Cells
In this step, cells are gets separated from each other to disrupt their normal relationship from neighbouring cells.
This disaggregation can be achieved by- By Chemical Method: many enzymes are used for this e.g. trypsin, collagenase, dispase.
- By Mechanical Method: by using tissue homogenizers.
(c) Subculturing of Cells
When the cells of primary culture has grown up and achieved a proper growth state, they are subcultured to give them more nutritional support for continuous growth.
The subculturing is necessary step to maintain the cells in continuous growth phase, as after some time of primary culture, the cells consume the provided nutrients and due to lack of nutrients cells growth become stagnant and leads to death. Thus to maintain the cell viability, the cells are transferred into fresh culture media. For sub culturing, the cells from primary cell culture are harvested / isolated and transferred to fresh culture media. Before sub culturing cells can be preserved in DMSO (di-methyl sulfoxide) or glycerol by cryopreservation technique.Types of Cell Culture
On the basis of source, number of subcuturing and the properties of subcultured cells, animal cell culture can be of following types:- Primary cell culture – When the cells are surgically removed from an organ, were placed into a suitable culture medium, so that they can attach, divide and grow. To obtain a primary cell culture, tissue is cut into small fragments and enzymatically (by using enzyme pepsin, collagenase) digested / separated into single cells. Many cells lost their viability, but many of them starts to grow and divide to form new cells. If the cells multiply repeatedly and grow for a long time, these cells can also then put in plastic bottles with fresh culture media. These cells are termed as primary cell lines.
- Established cell line culture – When the primary cell lines continue to grow and divide, they are sub cultured in fresh media to maintain their viability and growth. After many subculturing (about ≈70 - 80 times) these cells are called established cell lines. Primary cell lines can grow very slowly, but established cell lines grow faster, as there are some alterations in cell metabolic mechanism due to many subculture steps. Primary cell maintains the properties of parent cells, but established cell lines have some altered properties.
- Transformed cell line culture – With subsequent subculturing (more than 80 times), established cell lines cells become immortal (i.e. cells have the capacity to grow indefinitely). Normal cells have a limited growth capacity, but some cells acquire a capacity of growth for indefinite time. This capacity is generated due to transformation in genetic material, due to this transformation, cells lose the sensitivity to external stimuli and also sometime show changes in chromosomal numbers.

Types of Media
Various types of media are used for cell culture methods. They are generally categorized in two broad groups.- Natural Media – media components are from the natural origin that provide sufficient nutritional support for proliferation of animal cells. e.g. clots, biological fluids, tissue extracts, etc. These are of following types
- Plasma Clots: Prepared by mixing 15 drops of plasma with five drops of embryo extract in a watch glass.
- Biological Fluids: The various biological fluids used as culture medium (e.g. amniotic fluid, pleural fluid, aqueous humour from eye etc). serum is widely used, obtained from adult human blood, horse and calf blood.
- Tissue Extracts: Chick embryo extract is most commonly used, but bovine embryo extract is also used. Others are spleen, liver, bone marrow, leucocytes extract etc.
- Artificial Media – They are chemically synthesized e.g. serum containing media, serum free media, chemically defined media, protein free media etc. Synthetic media were prepared artificially by adding several nutrients (organic and Inorganic), viatmins, salts, oxygen and Carbon dioxide gas phase, serum proteins, carbohydrates, co-factors etc. Different types of media and their composition is defined accoding to their uses. Synthetic media are of two types.
- Serum free Media: these kind of synthetic media are devoid of serum. Crude protein fractions, such as bovine serum albumin, or α- and β- globulin are used as nutritional supplements. They include serum extract (not serum), Tissue extract or tissue hydrolysate, growth factors, hormones, carrier proteins like albumin and transferrine, lipids, metal ions, vitamins, poly-amines etc.
- Serum Containing Media: Serum contains a complete set of essential growth factors, binding and transportion proteins, human and bovine serums etc. Serum serves as source of amino acids, proteins, vitamins, growth factors, lipids and other nutritional supplements. It also supress effect of shere stress to protect cells from physical damage.
Cell Culture Techniques
Anchorage dependent cell culture -
Some tissue cells need attachment for growth are anchored dependent cells i.e. cells from kidney. All normal tissue derived cells are anchorage dependent cells and need surface or any support for their proliferation. In the absence of any support surface, animal anchorage dependent cells growth is arrested and cells gets destroyed due to induction of programmed cell death. These cells are sensitive to shear stress, and these cell require cell to cell communication and interaction and cell signalling pathway for their survival.Anchorage Independent Cell culture -
Cells which does not require attachment for growth or do not attach to the surface of the culture vessel are anchored independent cells e.g. lymphocytes. Cells derived from haematopoietic system and transformed cells like cancer (myeloma cells) are non-anchorage dependent cells and does not require any surface or support for growth, they well proliferate in freely suspended form of culture. Because in this form they get more nutritional material for better growth.Applications of Animal Cell Culture
- Drug screening and development- to establish the potential use of any therapeutic agent, the drug screening is essential. Once the chemical or any molecule formulated for the treatment of any disease, its efficacy and potency is checked before its commercial production. Cultured cells are exposed to chemical to be tested and studied its effect, and cell response to it.
- Cell based manufacturing - the cultured cells can be used to produce many important products. Cells are cultured and genetically modify to produce monoclonal antibodies, insulin and certain other hormones and biomolecules.
- Cell culture is also use to replace damaged tissue -by using culture of stem cells, many organs can be develop and implant in body i.e. skin, bone marrow, kidney, liver etc.
- Production of vaccines - cells are used to produce vaccines. In industry various microbial strains are used to grow in artificial culture media to produce vaccines, these include polio, hepatitis, rabies, chicken pox vaccines.
- Monoclonal antibody - production - Transformed cells are also used to produce monoclonal antibodies for passive immunization.
- Toxicity studies - cultured cells are widely used alone or with animals to study the therapeutic and toxic effects of drugs, cosmetics and other chemicals. These studies helps in development of dose fixation studies of any therapeutic agent.
- Cancer research - cultured animal cells are transformed into cancer cells and examined for therapeutic effects of any drug or chemical agent or any other method. This helps to develop any technique, method or any drug for cancer treatment.
- Virology - cultivation and study of viral cells is called virology. Virus are cultured for vaccine production, genetic engineering and to study their infection pathology.
- Genetic engineering -cells cultured in artificial media are used for genetic engineering or manipulation in genetic material (DNA and RNA). Genetic engineering includes isolation, combination, transfer of genetic material into new cells or genetically defective cells by the use of vectors and plasmids.
- Gene therapy - it is used to treat genetic diseases by gene delivery. Cultured cells are used for this study in which the genes are transfer via viral or non-viral methods.
Animal cell culture has several uses in pharmaceutical industry and research as production of valuable bio molecules and in research to study cell behaviour. It is also used in the treatment of various genetic and non-genetic diseases.